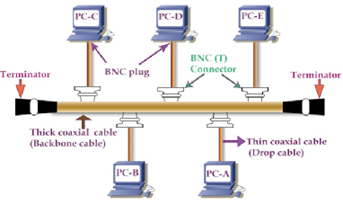
Coaxial Cables :
Thin Coaxial Cable :


- Thin coaxial cable popular as Thinnet or 10 BASE 2.
- It is about 0.2 inches (5mm) in diameter, flexible, and easier to install.
- It supports cable lengths up to 185 meters in a single segment.
- It is more prone to interference and signal attenuation than thick cable. It is not a robust cable.
- It uses BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors and T-connectors to connect computers to the network.
- It is less expensive, lightweight, and easier to handle and route.
Thick Coaxial Cable :

- Thick coaxial cable also popular as Thicknet 10 BASE 5 About 0.5 inches (12.7mm) in diameter, rigid. It is less flexible, and more challenging job to install.
- It supports longer runs—up to 500meters per segment without great signal loss.
- It offers better resistance to signal loss (attenuation) and interference.
- It uses ExternalTransceivers (AUI) and vampire taps to physically attach to the network—these are more complex and harder to install.

- It is more expensive due to size and additional installation difficulty, but suitable for large, professional environments or backbone installations.
- Used as backbone cabling in large buildings or campuses during the early days of Ethernet networking.